General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)

In a world where personal data has become a valuable commodity, the importance of safeguarding the privacy of individuals is paramount. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) represents the European Union's robust response to this challenge, setting the gold standard for data protection laws globally.
What Is The General Data Protection Regulation?
Established in 2018, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) seeks to provide EU citizens with greater control over their personal data, ensuring transparent, fair, and lawful processing by businesses and organisations. Whether it's an online retailer tracking shopping habits or a hospital storing patient records, the GDPR impacts all sectors and scales of data processing.
Why GDPR Matters?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) significantly enhances individual data rights, mandating stringent protections and greater transparency; it not only ensures individual data rights but also imposes heavy fines for non-compliance, underscoring its global influence on privacy standards.
- Individual Rights: GDPR empowers individuals, giving them rights to access, rectify, or delete their data. They can also object to certain types of processing and transfer their data to another service provider.
- Transparency: Organisations must clearly communicate how they're using personal data. No more long, unreadable terms and conditions.
- Data Breaches: GDPR introduces strict regulations on reporting data breaches. Companies can face hefty fines if they don't report a breach within 72 hours.
- Global Impact: Though an EU regulation, GDPR has a global reach. Any company, wherever they are located, that deals with the data of EU citizens must comply.
![]()
What Are The Seven Principles of GDPR?
GDPR's core principles ensure lawful, transparent, and secure processing of personal data, promoting fairness, accuracy, and respect for privacy across all data interactions.
Lawfulness, Fairness, and Transparency
- You must identify valid grounds under the UK GDPR (known as a ‘lawful basis’) for collecting and using personal data.
- You must ensure that you do not do anything with the data in breach of any other laws.
- You must use personal data in a way that is fair. This means you must not process the data in a way that is unduly detrimental, unexpected or misleading to the individuals concerned.
- You must be clear, open and honest with people from the start about how you will use their personal data..
Purpose Limitation
- You must be clear about what your purposes for processing are from the start.
- You need to record your purposes as part of your documentation obligations and specify them in your privacy information for individuals.
- You can only use the personal data for a new purpose if either this is compatible with your original purpose, you get consent, or you have a clear obligation or function set out in law.
Data Minimisation
- You must ensure the personal data you are processing is
- adequate – sufficient to properly fulfil your stated purpose;
- relevant – has a rational link to that purpose; and
- limited to what is necessary – you do not hold more than you need for that purpose.
Accuracy
- You should take all reasonable steps to ensure the personal data you hold is not incorrect or misleading as to any matter of fact.
- You may need to keep the personal data updated, although this will depend on what you are using it for.
If you discover that personal data is incorrect or misleading, you must take reasonable steps to correct or erase it as soon as possible. - You must carefully consider any challenges to the accuracy of personal data.
Storage Limitation
- You must not keep personal data for longer than you need it.
- You need to think about – and be able to justify – how long you keep personal data. This will depend on your purposes for holding the data.
- You need a policy setting standard retention periods wherever possible, to comply with documentation requirements.
- You should also periodically review the data you hold, and erase or anonymise it when you no longer need it.
- You must carefully consider any challenges to your retention of data. Individuals have a right to erasure if you no longer need the data.
- You can keep personal data for longer if you are only keeping it for public interest archiving, scientific or historical research, or statistical purposes.
Integrity and Confidentiality
- You must ensure that you have appropriate security measures in place to protect the personal data you hold.
- This is the ‘integrity and confidentiality’ principle of the GDPR – also known as the security principle.
Accountability
- The accountability principle requires that you take responsibility for what you do with personal data and how you comply with the other principles.
- You must have appropriate measures and maintain records to be able to demonstrate your compliance to these standards.
GDPR Compliance: A Multi-Step Journey
Achieving and maintaining GDPR compliance is a rigorous process. It demands commitment, thorough understanding, and continuous monitoring. Here's a breakdown of the critical steps:
- Data Assessment: Understand what personal data your organization holds, why it's held, and on what grounds.
- Gap Analysis: Identify where your current data practices fall short of GDPR requirements.
- Implementation: Modify processes, policies, and systems to address these gaps.
- Training & Awareness: Ensure all staff understand GDPR and their responsibilities.
- Ongoing Monitoring & Audits: Regularly review and update your practices to ensure continuous compliance.
Also make sure you read our 12 steps to GDPR Compliance Guide, for more details in implementing GDPR.
GDPR Enforcement and Penalties
One of the key features that sets the GDPR apart from previous data protection regulations is its teeth – the ability to impose significant penalties on those who fail to comply.
Fines and Penalties:
Organisations found in breach of GDPR can be fined up to 4% of their annual global turnover or €20 million, whichever is greater. The amount of the fine depends on the severity of the breach, and whether the company took compliance and security measures.

Factors Influencing Penalties:
- Nature of infringement: Was it a one-off mistake, or consistent negligence?
- Intention: Was the breach deliberate or accidental?
- Mitigation: Did the organization take any steps to mitigate the damage suffered by individuals?
- Preventative measures: Were there any procedures in place to prevent breaches?
- History: Have there been previous infringements by the organization?
Rights of Individuals under GDPR
The GDPR is largely about empowering individuals to have more control over their personal data. Let's delve into these rights in detail:
- Right to Access: Individuals can ask organizations if their data is being processed, where, and for what purpose. They also have the right to receive a copy of this data, free of charge, in an electronic format.
- Right to Rectification: Individuals have the right to have their personal data corrected if it's inaccurate or incomplete.
- Right to Erasure (Right to be Forgotten): This allows individuals to request the removal of their personal data from an organization's records, under specific circumstances.
- Right to Restrict Processing: Under certain conditions, individuals can request to block or suppress processing of their personal data.
- Right to Data Portability: Individuals can obtain and reuse their personal data across different services. This ensures they can easily transfer their data between service providers.
- Right to Object: In certain situations, individuals can object to their personal data being processed. This includes, for example, the processing of data for direct marketing purposes.

GDPR for Businesses: Best Practices
For businesses and organizations, being GDPR compliant is not just about avoiding penalties, but also building trust with customers and partners. Here are some best practices:
- Appoint a Data Protection Officer (DPO): Especially for larger organizations, having a dedicated DPO ensures you're continuously meeting GDPR standards.
- Implement Privacy by Design: Make data protection a priority from the start of any project, rather than an afterthought.
- Stay Informed: The digital landscape is ever-changing. Regularly update yourself with any GDPR amendments or relevant interpretations.
- Engage with Vendors: Ensure your third-party vendors are also GDPR compliant. They can be a potential risk if they mishandle the data they process on your behalf.
- Regular Training: Ensure every member of your organization understands the basics of GDPR and the importance of data protection.

Conclusion
GDPR has reshaped the way organisations across the globe approach data privacy. While it may seem overwhelming initially, with the right understanding and commitment, businesses can not only comply but thrive, ensuring they offer the best in data protection to their users.
ProCheckUp's GDRP Compliance Solutions:
ProCheckUp's GDPR Engagement Model - For Small Corporates
- IASME Cyber Essentials: A certification that verifies basic cyber-security hygiene, ensuring that financial institutions have fundamental security controls in place to protect against common cyber threats. (Learn More)
- IASME Cyber Assurance: This includes a GDPR readiness assessment to ensure that all aspects of data privacy and security are addressed, thus aligning with the GDPR’s stringent requirements.(Learn More)
ProCheckUp's GDPR Engagement Model - For Large Corporates
Scoping
In order for ProCheckUp to conduct a suitably detailed assessment on a company, it is essential to understand which Data environment's and processes are to be assessed. This understanding is achieved through a scoping exercise conducted between the client (and any relevant third parties involved), the technical consultant who will be conducting the assessment as well as the dedicated Account Manager. One of the most crucial elements of this process is understanding the overall outcome the client wishes to achieve. With this in mind, the entire engagement can be tailored to reach the objectives of the client.
The diagram below illustrates the full methodology of the GDPR Engagement with ProCheckUp.
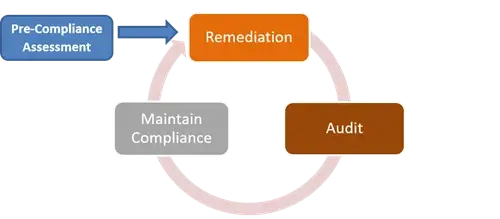
Phase one. Pre-Compliance Assessment
The pre-compliance assessment involves understanding the size of the compliance risk to your business, to determine where you stand, and create a compliance programme tailored to your specific requirements. This involves gathering data to identify gaps within your current security posture, GDPR and any other security standards where applicable.
The pre-compliance assessment will typically include:
- Conducting an on-site review of IT infrastructure, network design and architecture, application architecture, policies, procedures and processes;
- Identifying your sensitive data environment (stores locations) and determining your data flows;
- What personal data the company possesses;
- Where it is transferred to (third parties) and backup/storage;
- How it is secured/marked through the lifecycle;
- Performing vulnerability assessment scans that adhere to industry good practice;
- A gap analysis between the pre-assessment of the policies, procedures and processes as well as scan results against both industry best practice and the requirements of the EU GDPR;
- A risk analysis and recommendations report;
- Scoping and prioritising remediation activities.
Phase two. Remediation
Based upon the results of the pre-compliance assessment, the remediation programme provides a controlled, focused, and effective framework towards achieving compliance. Our remediation programme will help your organisation develop, implement and document the evidence required to prove compliance in accordance with the EUGDPR. We will look to form close working relationships with your organisation and any third-party vendors that are involved in delivering hardware, software and services.
Phase three. Audit and report on compliance
This phase will involve a formal audit process and include the production of the Report on Compliance to the EU GDPR.
Phase four. Maintaining Compliance
Achieving compliance isn’t just a one-off exercise but a continued journey.
It is vital that with any process or technology decisions are taken with compliance in mind. ProCheckUp can assist by managing the overall process, providing programme management from the initial pre-compliance assessment through to ongoing compliance.
To book an impact assessment about how GDPR will affect your business or for anything GDPR-related, contact us at gdpr@procheckup.com
For More Information Please Contact Us

ACCREDITATIONS







