ISO27001 ANNEX A: A Deep Dive into Controls and Objectives
ISO/IEC 27001, as the global standard for information security, has been heralded as a benchmark for companies aiming to demonstrate their commitment to safeguarding sensitive data. Annex A of ISO27001 is particularly noteworthy, serving as a comprehensive list of controls designed to address specific risks.

A Quick Overview of ISO27001 Annex A
Annex A of ISO27001 enumerates the list of controls, and the associated objectives, that organizations can adopt based on their risk assessment outcomes. It's important to understand that not all controls in Annex A need to be implemented. Instead, their relevance is determined by the organization's unique risk environment.
Implementing Annex A Controls: A Step-by-Step Approach
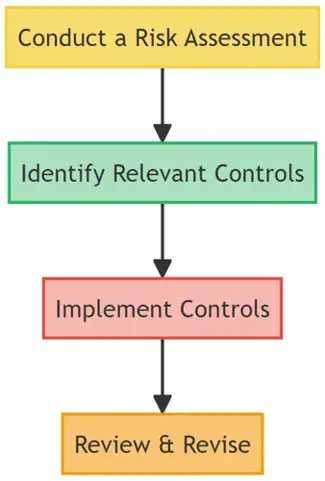
Successfully incorporating the controls from Annex A requires a structured approach:
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Understand the threats and vulnerabilities specific to your organization.
- Identify Relevant Controls: Based on the risk assessment, select the controls from Annex A that are most relevant.
- Implement Controls: With the help of IT, security, and business teams, put these controls into practice.
- Review & Revise: Regularly revisit the controls to ensure they remain effective and relevant.
Diving Deep into Annex A Domains
Annex A is categorized into various domains, each focusing on specific aspects of information security:
- A.5: Information Security Policies
Outlines the need for appropriate security policies, reviewed and updated regularly. - A.6: Organization of Information Security
Addresses the division of responsibilities and collaboration across different parts of the organization. - A.7: Human Resource Security
Ensures employees, contractors, and third-party users understand their responsibilities and are suitable for the roles they are considered for.

A.8: Asset Management
The main goal of this domain is to identify assets and define appropriate protection responsibilities.
- A.8.1: Responsibility for Assets
Ensure that assets receive an appropriate level of protection by assigning a custodian for each. - A.8.2: Information Classification
Classify information and assets in accordance with their value, legal standing, sensitivity, and criticality to the organization. - A.8.3: Media Handling
Set protocols for handling, transporting, and disposing of media containing information.
A.9: Access Control
This domain is all about ensuring that access to assets is authorized and can be controlled.
- A.9.1: Business Requirement of Access Control
Document and regularly review the access control to different information and systems, aligning it with business requirements. - A.9.2: User Access Management
Ensure a formal user registration and de-registration process to grant and revoke access to all information systems and services. - A.9.3: User Responsibilities
Make users accountable for safeguarding their authentication information.

A.10: Cryptography
This domain emphasizes the importance of effective cryptographic measures to secure sensitive data.
- A.10.1: Cryptographic Controls Policy
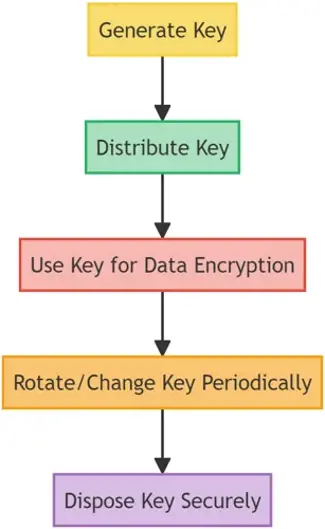
Design, implement, and manage cryptographic controls based on the organization's risk appetite and in compliance with legal and regulatory requirements. - A.10.2: Key Management
Protect, store, distribute, and periodically change cryptographic keys to ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
A.11: Physical and Environmental Security
One of the fundamental pillars of information security, this domain ensures the physical security of data and systems.
- A.11.1: Secure Areas
Develop protocols to prevent unauthorized physical access, damage, and interference to the organization's premises and information. - A.11.2: Equipment
Ensure protection against threats, both external and environmental, to prevent loss, damage, or compromise of assets.
A.12: Operations Security
A focus on preventing and detecting security events through effective operations.
- A.12.1: Operational Procedures and Responsibilities
Regularly document and review operating procedures to maintain a secure operational environment. - A.12.2: Protection from Malware
Employ defense mechanisms to detect and prevent malware across the organization.

A.13: Communications Security
This domain is pivotal in securing an organization's communication touchpoints.
- A.13.1: Network Security Management
Implement network security controls to protect information systems. - A.13.2: Transfer of Information
Formulate security measures to protect information when being transferred both within and outside of the organization.
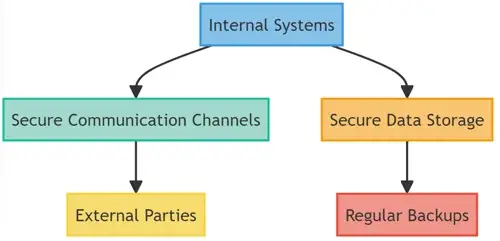
A.14: System Acquisition, Development, and Maintenance
This domain emphasizes the security aspects during the entire lifecycle of information systems, from initial requirements to disposal.
- A.14.1: Security Requirements of Information Systems
Define and embed security requirements based on information risk when procuring or developing systems. - A.14.2: Secure Development
Implement secure coding practices and review software updates to detect and rectify vulnerabilities. - A.14.3: Test Data
Protect and separate test data from operational systems to ensure there is no unintended exposure.
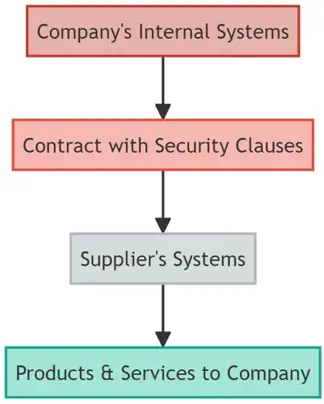
A.15: Supplier Relationships
Businesses often work with external partners; this domain ensures those partnerships don’t pose undue risk.
- A.15.1: Information Security in Supplier Relationships
Incorporate security clauses in contracts with suppliers to ensure they maintain comparable security standards. - A.15.2: Addressing Security within Supplier Agreements
Define the roles and responsibilities concerning the security of the provided products and services.
A.16: Information Security Incident Management
Responding to and managing security incidents is a critical aspect of maintaining information security.
- A.16.1: Management of Information Security Incidents and Improvements
Create and maintain an incident response plan. Ensure lessons learned from breaches or incidents are fed back into the organization's processes.

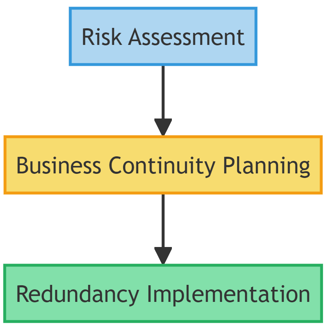
A.17: Information Security Aspects of Business Continuity
When disaster strikes, organizations need to be ready. This domain focuses on the security components of business continuity plans.
- A.17.1: Information Security Continuity
Ensure that information security continuity is an integral part of the organization's business continuity management systems. - A.17.2: Redundancies
Establish redundancies for critical information assets to prevent disruptions from unplanned outages or cyber-attacks.
A.18: Compliance
Compliance isn't just about adhering to external regulations. It's also about ensuring internal security policies are followed consistently.
- A.18.1: Compliance with Legal and Contractual Requirements
Regularly review and update the organization's adherence to legislative, regulatory, and contractual requirements. - A.18.2: Information Security Reviews
Conduct regular reviews of the organization's approach to information security, ensuring it remains effective and relevant.

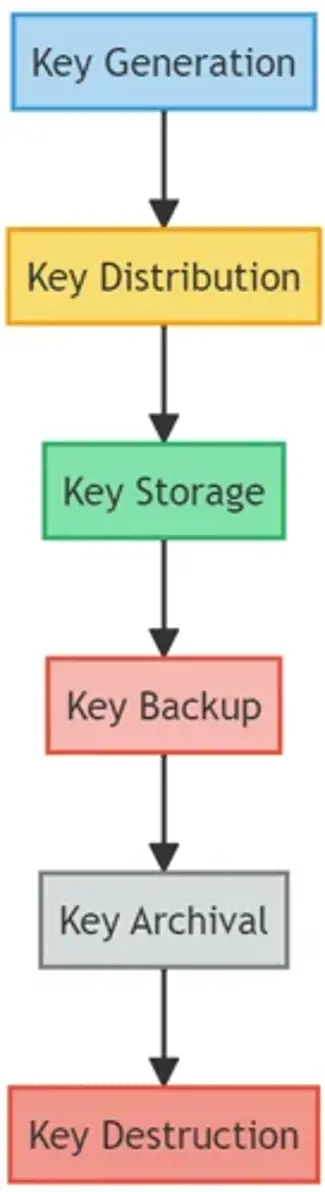
A.19: Cryptographic Controls
In an era of rising cyber threats, encrypting sensitive data is not just an option but a necessity. This domain emphasizes the use of cryptographic methods to safeguard data in transit and at rest.
- A.19.1: Key Management
Ensure proper generation, distribution, storage, backup, archival, and destruction of cryptographic keys to prevent unauthorized access or use.
A.20: Relations with Suppliers
Every organization relies on a network of suppliers and partners. It's essential to ensure that these external entities maintain the same security standards.
- A.20.1: Addressing Security within Supplier Agreements
Incorporate security clauses and expectations into contracts and agreements with third parties, ensuring that data is handled with the utmost care.

Conclusion
Understanding ISO27001's Annex A is critical for any organization that wishes to establish a robust and comprehensive security posture. By adhering to its guidelines, businesses can ensure they're not only protecting themselves but also staying ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of cyber-security.
For More Information Please Contact Us

ACCREDITATIONS






