Introduction
In the digital age, phishing has emerged as a prevalent threat to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), exploiting the human factor to breach defences and extract sensitive information. This guide delves into the essence of phishing, its various forms, and actionable strategies for SMEs to fortify their defences against these insidious attacks.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a cyber deception technique involving fraudulent communications, seemingly from reputable sources, aimed at stealing sensitive data or deploying malware. Its simplicity and effectiveness have made it a favourite among cyber criminals, posing a significant risk to individuals and organizations alike.
How Phishing Works
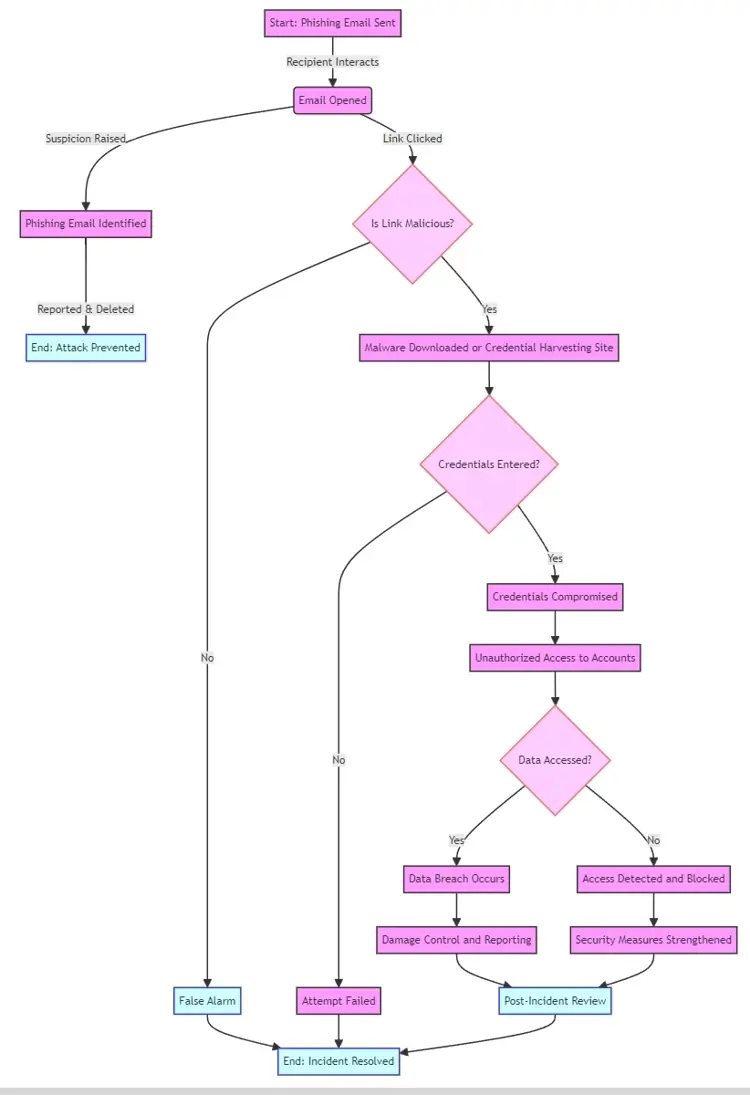
Initial Contact: Attackers cast a wide net, sending out emails designed to mimic those from trusted entities.
Deceptive Appeal: These emails often contain urgent calls to action, prompting the recipient to click a link or download an attachment.
Malicious Outcome: Following these instructions can lead to malware installation or redirection to counterfeit websites where personal information is harvested.
Phishing Flowchart
Types of Phishing
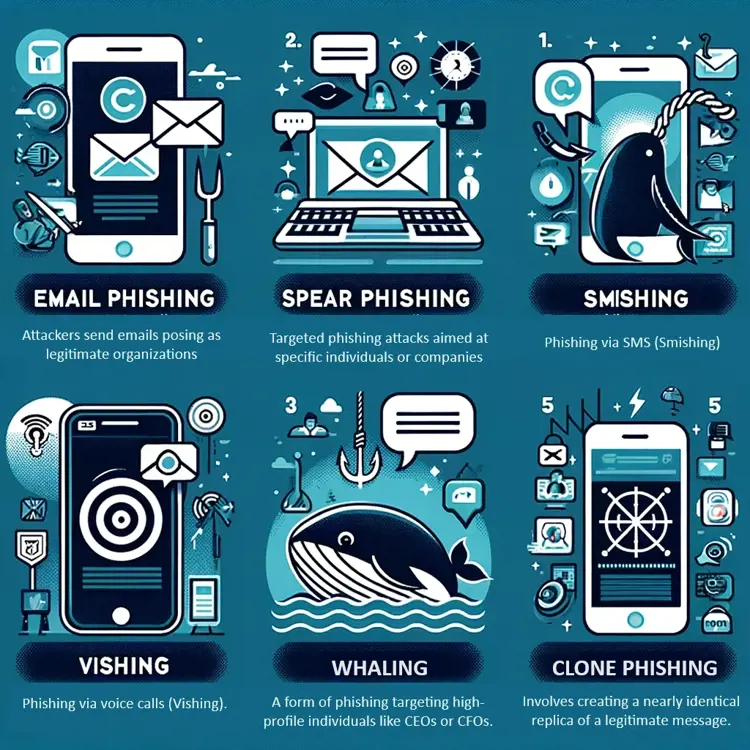
Email Phishing: The broadest category, characterized by mass emails posing as well-known organizations.
Prevention Tips: Verify sender details, be wary of generic greetings, and scrutinize for urgency that demands immediate action.
Spear Phishing: Highly targeted, leveraging personal information for credibility.
Prevention Tips: Double-check emails requesting confidential data, even from familiar sources.
Smishing and Vishing: Phishing conducted via SMS or voice calls, respectively.
Prevention Tips: Never disclose personal information in response to unsolicited texts or calls.
Whaling: Targets high-profile individuals with tailored messages.
Prevention Tips: Implement multi-factor authentication and conduct security awareness training for executives.
Clone Phishing: Involves duplicating legitimate messages with malicious alterations.
Prevention Tips: Verify the authenticity of messages, especially those with unexpected links or attachments.
Common Phishing Tactics
Domain Spoofing: Creating fake sites or emails that mimic legitimate ones.
Link Manipulation: Embedding harmful links under the guise of benign ones.
Social Engineering: Manipulating individuals into voluntarily giving up confidential information.
Evolution and Future Trends in Phishing
Mobile and Social Media Phishing: Exploiting the ubiquity of smartphones and the trust in social networks.
AI in Phishing: Utilising artificial intelligence to craft more convincing phishing messages.
Future Trends: Expect more sophisticated, AI-powered attacks targeting specific individuals or organizations.
Impact of Phishing
Financial Losses: Direct financial damage and potential fines for data breaches.
Data Breaches: Exposure of sensitive personal and corporate information.
Reputational Damage: Erosion of customer trust and potential loss of business.
How to Spot Phishing Attacks
Identifying phishing attempts is crucial in protecting your organization from potential threats. Here are detailed insights on spotting these deceptive communications:-

1. Unusual Sender Email Addresses
Legitimacy Check: Compare the sender's email with official communication channels. Phishers often use addresses that mimic legitimate ones with slight alterations.
2. Generic Greetings and Urgent Language
Personalisation: Legitimate emails from companies you do business with often use personalized greetings. Phishing emails typically start with generic phrases like "Dear Customer."
Sense of Urgency: Phishing attempts create a sense of urgency, pressuring recipients to act quickly, often threatening account suspension or other negative consequences.
3. Spelling and Grammar Mistakes
Professional Standards: Reputable organizations have high standards for communication. Obvious spelling and grammar errors in an email suggest it's a phishing attempt.
4. Suspicious Links and Attachments
Hover Technique: Hover over any links without clicking. If the URL looks suspicious or doesn't match the supposed destination, it's likely a phishing attempt.
Unexpected Attachments: Be wary of unsolicited attachments, especially from unknown senders. These can contain malware or ransomware.
5. Requests for Sensitive Information
Information Sharing: Legitimate companies will never ask for sensitive information via email. Any request for passwords, financial details, or personal information should be considered a red flag.
How to Prevent Phishing Attacks

Preventing phishing attacks requires a combination of technology, education, and processes. Here's how SMEs can fortify their defences:
1. Implement Email Authentication Protocols
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC: These email authentication methods help prevent spoofing by verifying that the sender is authorized to send emails from the domain.
2. Use Phishing Detection Software
Machine Learning Algorithms: Modern phishing detection tools analyse email content for phishing indicators, alerting users to potential threats.
3. Deploy Secure Email Gateways
Email Filtering: Secure email gateways filter incoming emails, blocking phishing attempts and other malicious communications before they reach the user.
4. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Additional Security Layer: MFA requires a second form of verification beyond just a password, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access even if login details are compromised.
5. Regular Software and Security Updates
Patch Management: Keeping all systems and security software updated ensures protection against the latest threats, including those used in phishing attacks.
6. Employee Training and Awareness Programs
Regular Training: Conducting regular training sessions on the latest phishing tactics and how to recognize them is crucial. Employees should know how to handle suspicious emails.
Simulated Phishing Exercises: Simulating phishing attacks can test employees' awareness and help identify areas where additional training is needed.
7. Advanced Email Filtering Solutions
Beyond Basic Filters: Advanced solutions offer deeper analysis of email content, including embedded links and attachments, to identify and block sophisticated phishing attempts.
8. Incident Response Planning
Preparedness: Having a clear plan in place for responding to confirmed phishing attacks helps minimize damage. This includes steps for isolating affected systems, changing passwords, and notifying affected parties.
Legislation and Compliance
GDPR: Emphasises the protection of personal data..
Sector-Specific Regulations: Additional regulations for finance and healthcare to combat phishing.
Conclusion
Phishing remains a formidable threat, but awareness and proactive defence strategies can significantly mitigate its impact. SMEs, in particular, must prioritize cyber security education and implement robust measures to protect their assets and reputation in the face of evolving phishing tactics.




Categories